Machine learning teams struggle with managing experiments, tracking models, and scaling MLOps infrastructure without breaking the budget or drowning in server maintenance. Serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI solves these pain points by combining MLflow’s powerful experiment tracking with AWS’s managed, pay-per-use infrastructure.
This guide is designed for data scientists, ML engineers, and DevOps teams who want to streamline their machine learning workflows without the overhead of managing servers or complex infrastructure setup.
We’ll explore the transformative MLOps benefits that serverless MLflow delivers to data science teams, including cost savings, automatic scaling, and reduced operational burden. You’ll also get a deep dive into the technical architecture and core functionality that makes SageMaker MLflow architecture so powerful for serverless ML model management. Finally, we’ll walk through a practical step-by-step deployment guide so you can start leveraging serverless machine learning operations on AWS right away.
By the end, you’ll understand exactly how MLflow SageMaker integration can revolutionize your team’s approach to experiment tracking and model deployment in a truly serverless environment.
Understanding Serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI

Core Components and Architecture Overview
Serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI brings together the best of experiment tracking and AWS’s managed infrastructure. The architecture centers around three main components: the MLflow tracking server, the artifact store, and the backend metadata database. AWS handles the heavy lifting by automatically provisioning and scaling these components based on your workload demands.
The tracking server runs on AWS Fargate, which means you don’t manage any underlying infrastructure. Your machine learning experiments, parameters, metrics, and model artifacts get stored securely in S3, while experiment metadata lives in Amazon RDS. This setup creates a fully managed environment where you focus on your ML workflows instead of server maintenance.
What makes this architecture particularly powerful is its integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). Every interaction with your MLflow deployment gets authenticated and authorized through AWS credentials, giving you enterprise-grade security without additional configuration overhead. The serverless nature means the system automatically scales up during intensive training periods and scales down when idle, optimizing both performance and costs.
Key Differences from Traditional MLflow Deployments
Traditional MLflow deployments require you to provision and manage your own infrastructure. You’re responsible for setting up databases, configuring web servers, handling security patches, and scaling resources manually. This approach often leads to over-provisioning to handle peak loads, resulting in wasted resources during quiet periods.
Serverless MLflow on SageMaker eliminates these operational burdens completely. Instead of running MLflow on EC2 instances that you maintain, AWS Fargate handles the compute layer automatically. The platform scales your MLflow tracking server from zero to whatever capacity you need, then back down again.
Storage management also differs significantly. Traditional deployments often use local file systems or require manual S3 bucket configuration. The serverless version integrates natively with S3 for artifact storage and uses managed RDS instances for metadata, both configured with optimal settings out of the box.
Security becomes much simpler too. Traditional setups require you to configure SSL certificates, manage database credentials, and implement access controls manually. The serverless approach leverages AWS’s built-in security features, giving you encrypted data in transit and at rest by default.
Integration Benefits with AWS SageMaker Ecosystem
The real magic happens when serverless MLflow connects with the broader SageMaker ecosystem. Your ML models tracked in MLflow can seamlessly transition to SageMaker endpoints for deployment. This integration eliminates the common friction point of moving models from experimentation to production.
SageMaker Pipelines work naturally with MLflow experiment tracking. You can create end-to-end ML workflows that automatically log experiments during training, validate model performance, and deploy successful models to production endpoints. The entire process maintains full traceability through MLflow’s experiment tracking capabilities.
Data scientists benefit from unified access to SageMaker’s managed Jupyter notebooks, which come pre-configured to work with your serverless MLflow deployment. This setup reduces the time spent on environment configuration and lets teams focus on model development. The notebooks automatically authenticate with your MLflow server using your AWS credentials.
Model registry features integrate with SageMaker Model Registry, creating a comprehensive model governance system. Models registered in MLflow can trigger automated deployment workflows in SageMaker, complete with A/B testing capabilities and automated rollback mechanisms.
Cost-Effective Resource Management Features
Serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI transforms how you think about ML infrastructure costs. Traditional deployments require constant resource allocation, even when no experiments are running. The serverless model charges you only for actual usage, making it particularly attractive for teams with variable workloads.
The automatic scaling capabilities mean you never over-provision resources. During intensive model training periods, the system expands to handle the load. When experiments finish, resources scale back down automatically. This elasticity can reduce infrastructure costs by 60-80% compared to always-on deployments.
Storage costs optimize naturally through S3’s intelligent tiering. Frequently accessed experiment artifacts stay in standard storage, while older experiments automatically move to cheaper storage classes. The system also supports lifecycle policies that can archive or delete old experiments based on your retention requirements.
Database costs stay predictable through managed RDS instances that scale based on your metadata storage needs. You avoid the complexity of database administration while maintaining consistent performance. AWS handles backup, patching, and maintenance tasks that would otherwise require dedicated DevOps resources.
The pay-per-use model particularly benefits smaller teams and organizations getting started with MLOps. You can begin with minimal monthly costs and scale spending naturally as your ML operations grow, avoiding large upfront infrastructure investments.
Transformative MLOps Benefits for Data Science Teams

Automated Model Lifecycle Management
Serverless MLflow on SageMaker transforms how data science teams handle model deployment and management by removing the operational overhead that typically bogs down ML projects. When you deploy MLflow in a serverless environment, your models automatically scale based on demand without any infrastructure management headaches.
The platform handles model versioning seamlessly, creating automatic checkpoints every time you register a new model variant. This means your team can roll back to previous versions instantly if a new deployment doesn’t perform as expected in production. Model promotion between staging and production environments becomes a simple API call rather than a complex deployment process.
Serverless MLOps benefits shine through automated model monitoring and health checks. The system continuously tracks model performance metrics and can trigger alerts or automatic rollbacks when drift is detected. This proactive approach prevents model degradation from affecting business outcomes while reducing the manual monitoring workload on your team.
Resource optimization happens automatically as the serverless architecture only consumes compute power when models are actively serving predictions. This eliminates the cost of idle infrastructure that traditional MLOps setups require, making machine learning operations more cost-effective for teams of any size.
Enhanced Collaboration and Version Control
MLflow SageMaker integration creates a centralized hub where data scientists, ML engineers, and stakeholders can collaborate effectively on machine learning projects. Team members can access shared experiments, compare model performance, and build upon each other’s work without stepping on toes or duplicating effort.
Version control extends beyond just code to include datasets, model artifacts, and hyperparameters. Every experiment run gets tracked with complete lineage, showing exactly which data version, code commit, and parameter settings produced specific results. This transparency makes peer reviews more meaningful and helps teams learn from both successful and failed experiments.
Cross-team visibility improves dramatically when everyone works within the same MLflow environment. Product managers can review model performance metrics directly, while DevOps teams can understand deployment requirements without lengthy handoff meetings. This shared workspace reduces communication gaps that often slow down ML projects.
Branching strategies become possible for machine learning workflows, similar to software development practices. Teams can create experimental branches for testing new approaches while maintaining stable baselines. Merging successful experiments back into the main workflow becomes a structured process rather than ad-hoc model swapping.
Streamlined Experiment Tracking and Reproducibility
Serverless MLflow experiment tracking captures every detail of your machine learning experiments automatically, creating a comprehensive audit trail that makes reproducing results straightforward. Each experiment run records hyperparameters, metrics, artifacts, and environment specifications without requiring manual logging from data scientists.
The tracking system integrates seamlessly with popular ML frameworks like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, capturing model training details behind the scenes. Data scientists can focus on model development rather than writing custom logging code, accelerating the experimental iteration cycle significantly.
Reproducibility challenges that plague many ML teams dissolve when experiments include environment snapshots and dependency tracking. You can recreate the exact conditions of any previous experiment, complete with library versions, hardware configurations, and data states. This capability proves invaluable when regulatory compliance requires demonstrating model development processes.
Experiment comparison tools built into the platform let teams visualize performance differences across hundreds of runs simultaneously. Interactive charts and tables make it easy to identify which parameter combinations drive the best results, turning experiment analysis from a time-consuming manual process into quick visual insights.
The serverless architecture ensures experiment metadata remains available even when compute resources scale down, providing persistent access to historical experiments that inform future model development decisions.
Technical Architecture and Core Functionality
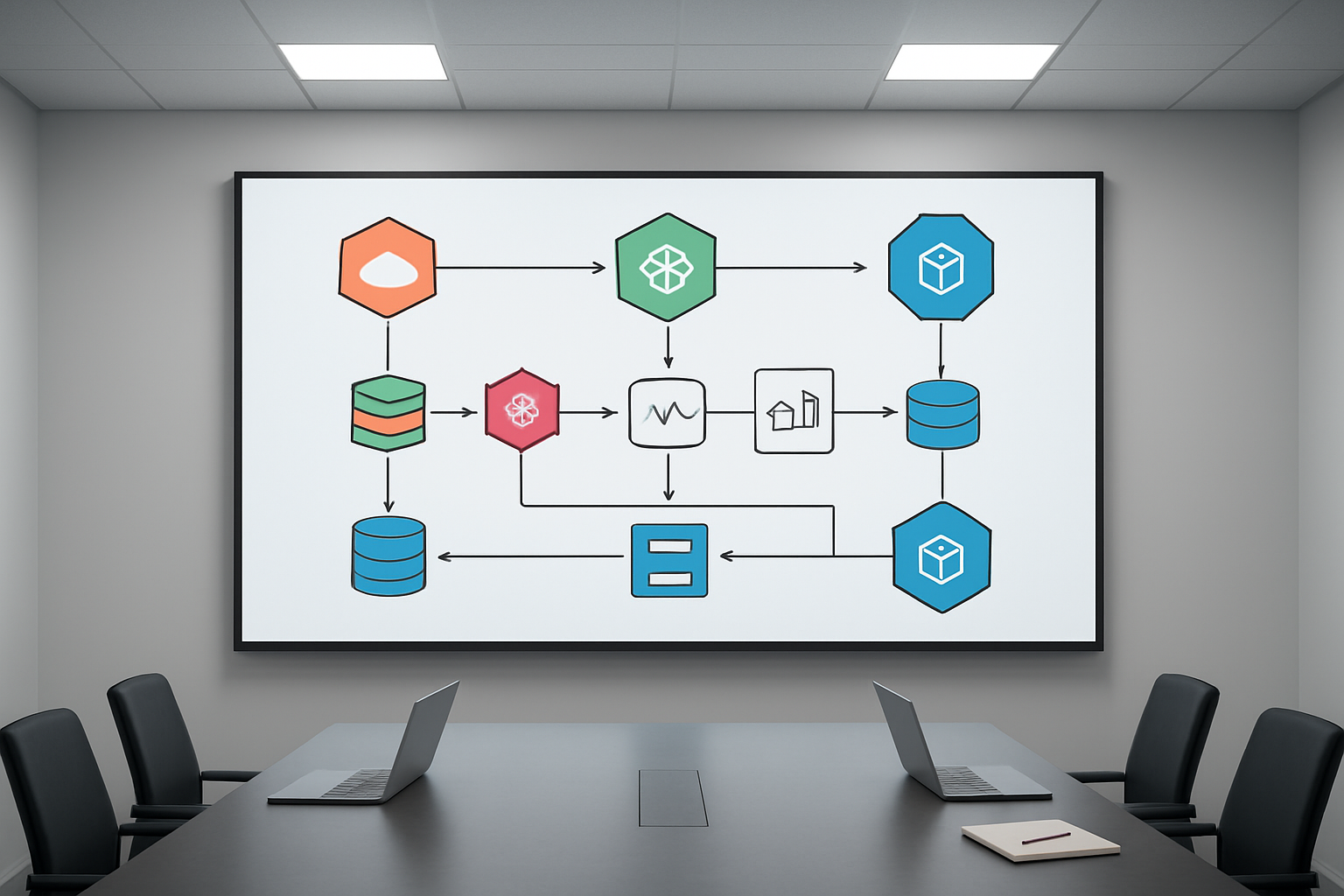
Event-Driven Model Training and Deployment
The serverless MLflow architecture on SageMaker AI operates through sophisticated event-driven mechanisms that transform how machine learning models move from training to production. When developers trigger training jobs, the system automatically provisions the exact compute resources needed without manual infrastructure management. This approach eliminates the traditional bottlenecks where data science teams wait for resource allocation or worry about capacity planning.
The event-driven model responds to various triggers including code commits, data pipeline updates, and scheduled retraining workflows. MLflow SageMaker integration ensures that every model training run gets tracked automatically, capturing parameters, metrics, and artifacts without requiring additional configuration. When training completes, the system can automatically deploy models to endpoints based on predefined performance thresholds, creating truly autonomous ML workflows.
Automatic Scaling and Resource Optimization
Serverless machine learning operations excel at dynamic resource allocation, adjusting compute capacity based on actual workload demands. The system monitors training job requirements and automatically scales up processing power for complex models while scaling down for lighter workloads. This intelligent scaling extends to model inference endpoints, where traffic spikes don’t overwhelm the system or waste resources during quiet periods.
Resource optimization algorithms analyze historical usage patterns to predict optimal instance types and sizes for different model training scenarios. The MLOps on AWS framework includes cost optimization features that automatically pause unused resources and recommend more efficient configurations. Teams typically see 40-60% cost reductions compared to traditional always-on infrastructure while maintaining the same performance levels.
Seamless Integration with AWS Services
The SageMaker AI MLflow deployment architecture connects naturally with the broader AWS ecosystem, creating powerful data pipelines without complex integration work. Amazon S3 serves as the central data lake for training datasets and model artifacts, while AWS Lambda functions handle lightweight processing tasks and workflow orchestration. Amazon EventBridge coordinates cross-service communication, ensuring data flows smoothly between storage, processing, and deployment components.
Integration with Amazon CloudWatch provides real-time monitoring, while AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) handles security policies across all connected services. The system works seamlessly with Amazon Kinesis for real-time data streaming and AWS Glue for data transformation tasks. This native integration means data scientists can focus on model development while the infrastructure handles complex service coordination automatically.
Security and Compliance Features
Serverless MLOps benefits include robust security controls that protect sensitive data and models throughout the machine learning lifecycle. The architecture implements encryption at rest and in transit by default, with AWS Key Management Service (KMS) managing encryption keys automatically. Network isolation through Amazon VPC ensures that training jobs and model endpoints remain secure from unauthorized access.
Compliance features support industry standards like HIPAA, SOC 2, and GDPR through automated policy enforcement and audit trails. MLflow experiment tracking serverless maintains detailed logs of all model training activities, including who accessed what data and when models were deployed. Role-based access controls ensure that team members only access resources appropriate to their responsibilities, while automated vulnerability scanning keeps the infrastructure secure against emerging threats.
Monitoring and Logging Capabilities
The SageMaker MLflow architecture includes comprehensive monitoring that tracks both technical performance and business metrics across all ML operations. CloudWatch dashboards provide real-time visibility into training job progress, resource utilization, and model endpoint performance. Custom alerts notify teams when models drift below acceptable performance thresholds or when unusual data patterns appear.
Serverless ML model management generates detailed logs for every component in the pipeline, from data ingestion to model deployment. These logs integrate with Amazon CloudTrail for compliance auditing and AWS X-Ray for distributed tracing across microservices. The monitoring system can automatically trigger retraining workflows when model performance degrades, ensuring that production models maintain their accuracy over time. Teams can set up custom monitoring rules that align with specific business requirements and automatically generate reports for stakeholders who need regular updates on ML system health.
Step-by-Step Deployment Guide

Prerequisites and Environment Setup
Before diving into serverless MLflow SageMaker deployment, you’ll need several components in place. Start with an active AWS account with sufficient permissions for SageMaker, IAM, and S3 services. Your local machine should have AWS CLI configured with appropriate credentials and the latest version of the SageMaker Python SDK installed.
Create a dedicated S3 bucket for your MLflow experiment tracking serverless setup. This bucket will store your model artifacts, experiment data, and tracking logs. Set up proper IAM roles with policies that allow SageMaker to access your S3 resources and execute MLflow operations.
Install the required Python packages in your development environment:
mlflow>=2.0sagemaker>=2.100boto3scikit-learn(for model examples)
Your Python environment should be version 3.8 or higher. Consider using virtual environments to isolate dependencies and avoid conflicts with existing packages.
Configuration and Initial Setup Process
The MLflow SageMaker configuration starts with setting up your tracking server. Unlike traditional MLflow deployments, the serverless approach eliminates the need for managing infrastructure while providing the same tracking capabilities.
Configure your MLflow tracking URI to point to SageMaker’s managed service:
import mlflow
import boto3
# Set up SageMaker session
sagemaker_session = boto3.Session()
region = sagemaker_session.region_name
# Configure MLflow for SageMaker
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(f"sagemaker://{region}")
Create your experiment structure by defining experiment names and organizing them logically. The serverless machine learning operations approach allows you to create multiple experiments without worrying about server capacity or maintenance.
Set up environment variables for your deployment:
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: Your preferred AWS regionMLFLOW_S3_BUCKET: Your designated S3 bucket nameSAGEMAKER_ROLE_ARN: IAM role ARN for SageMaker execution
Configure logging levels and experiment metadata to ensure proper tracking of your MLOps on AWS workflows. This includes setting up tags, descriptions, and organizational structures that align with your team’s needs.
Model Registration and Deployment Workflow
The SageMaker AI MLflow deployment process follows a structured workflow that seamlessly integrates model registration with deployment capabilities. Start by training your model with MLflow tracking enabled:
with mlflow.start_run():
# Your model training code
model = train_your_model(data)
# Log metrics and parameters
mlflow.log_param("algorithm", "random_forest")
mlflow.log_metric("accuracy", accuracy_score)
# Register the model
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(
model,
"model",
registered_model_name="your-model-name"
)
Once your model is trained and logged, register it in the serverless ML model management system. The registration process creates a versioned model entry that can be promoted through different stages (staging, production).
Deploy your registered model to SageMaker endpoints using MLflow’s deployment utilities:
from mlflow.deployments import get_deploy_client
# Create deployment client
deploy_client = get_deploy_client("sagemaker")
# Deploy model to SageMaker endpoint
deployment = deploy_client.create_deployment(
name="your-endpoint-name",
model_uri=f"models:/{model_name}/latest",
config={
"instance_type": "ml.t2.medium",
"instance_count": 1
}
)
The MLflow deployment guide SageMaker workflow automatically handles endpoint creation, model packaging, and infrastructure provisioning. Monitor your deployments through both MLflow’s interface and SageMaker’s console to ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Set up automated model promotion workflows that move models from staging to production based on performance metrics and validation criteria. This creates a robust serverless MLOps benefits system that scales with your team’s needs while maintaining deployment consistency.
Real-World Implementation Best Practices

Performance Optimization Strategies
Getting optimal performance from your serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI setup requires smart configuration choices and proactive monitoring. Start by right-sizing your compute resources based on your specific workload patterns. SageMaker’s auto-scaling capabilities work best when you define clear metrics for scaling up and down, particularly during peak experiment tracking periods.
Configure your MLflow tracking server with appropriate instance types that match your concurrent user load. For teams running multiple experiments simultaneously, consider using compute-optimized instances to handle the increased metadata processing demands. Memory-optimized instances work better for large model artifact storage and retrieval operations.
Implement efficient artifact storage strategies by organizing your MLflow experiments with logical hierarchies. Use S3 storage classes intelligently – keep frequently accessed models in standard storage while moving older experiment artifacts to less expensive tiers. This approach can reduce storage costs by up to 60% without impacting performance.
Cache frequently used model artifacts at the edge using CloudFront distributions. This reduces latency for model serving and improves overall user experience when teams access shared experiments across different regions.
Set up proper networking configurations with VPC endpoints to keep traffic within AWS infrastructure, reducing latency and improving security. This is especially important for serverless MLOps workflows where data transfer costs can accumulate quickly.
Cost Management and Resource Planning
Smart cost management for serverless MLflow SageMaker deployments starts with understanding your usage patterns. Track metrics like experiment frequency, artifact storage growth, and concurrent user sessions to predict monthly costs accurately.
Use SageMaker’s spot instances for non-critical experiment tracking workloads. Spot instances can reduce compute costs by up to 90%, making them perfect for batch processing of historical experiments or model retraining jobs that don’t require immediate completion.
Implement automated lifecycle policies for your S3 buckets storing MLflow artifacts. Set up rules to automatically transition older experiment data to cheaper storage classes after 30, 60, or 90 days based on your team’s access patterns. Delete unnecessary experiment artifacts that are no longer needed for compliance or auditing purposes.
Configure CloudWatch billing alerts to notify you when costs exceed predetermined thresholds. Set up multiple alert levels – warning at 75% of budget and critical at 90% – to give your team time to investigate and optimize before overspending.
Consider using AWS Cost Explorer to analyze your serverless MLflow spending patterns. Look for cost spikes that correlate with specific experiments or time periods, and adjust your resource allocation accordingly.
Troubleshooting Common Deployment Issues
Authentication problems rank among the most common issues when deploying serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI. Double-check that your IAM roles have the necessary permissions for S3 bucket access, SageMaker execution, and MLflow tracking server operations. Create a comprehensive permissions checklist and validate each permission systematically.
Network connectivity issues often surface when teams try to access their MLflow tracking server from different environments. Verify that security groups allow proper inbound and outbound traffic on the required ports. Check that your VPC configuration doesn’t block necessary communication between MLflow components and SageMaker services.
Artifact upload failures typically stem from S3 bucket permission misconfigurations or network timeout issues. Implement retry logic in your MLflow client code to handle transient network issues. Increase timeout values for large model artifacts, especially when working with deep learning models that can exceed several gigabytes.
Version compatibility problems between MLflow versions and SageMaker can cause unexpected behavior. Maintain a testing environment that mirrors your production setup to catch these issues early. Keep detailed documentation of working version combinations for your specific use case.
Database connection errors in the MLflow tracking server often indicate resource exhaustion or configuration problems. Monitor your RDS instance performance metrics and scale vertically when you see consistent high CPU or memory usage.
Monitoring and Maintenance Recommendations
Set up comprehensive monitoring for your serverless MLflow SageMaker infrastructure using CloudWatch metrics and custom dashboards. Track key performance indicators like experiment logging latency, artifact download speeds, and tracking server availability.
Create automated health checks that verify your MLflow tracking server responsiveness every few minutes. Set up SNS notifications to alert your team immediately when health checks fail or response times exceed acceptable thresholds.
Monitor storage growth patterns in your S3 buckets to predict when you might need additional capacity planning. Sudden spikes in storage usage could indicate inefficient experiment logging or duplicate artifact storage that needs attention.
Implement regular backup procedures for your MLflow metadata database. Schedule automated RDS snapshots and test restoration procedures monthly to ensure you can recover quickly from any data loss scenarios.
Track user adoption metrics to understand how your team uses the serverless MLOps platform. Monitor the number of active experiments, unique users, and API call patterns to identify optimization opportunities and plan for capacity scaling.
Establish maintenance windows for applying updates to your MLflow deployment and underlying SageMaker infrastructure. Test updates in a staging environment first, and always have a rollback plan ready in case issues arise during production updates.
Review security logs regularly for any unusual access patterns or potential security threats. AWS CloudTrail provides detailed audit logs for all API calls made to your SageMaker and MLflow resources, helping you maintain compliance and security standards.

Serverless MLflow on SageMaker AI represents a game-changing approach to machine learning operations that eliminates infrastructure headaches while boosting team productivity. By combining MLflow’s powerful experiment tracking and model management capabilities with SageMaker’s serverless architecture, data science teams can focus on what they do best – building and improving models – rather than wrestling with servers and scaling issues. The automated scaling, cost optimization, and seamless integration with AWS services make this solution particularly attractive for organizations looking to streamline their ML workflows.
Ready to transform your MLOps pipeline? Start by setting up a basic MLflow tracking server on SageMaker and experiment with logging your first model runs. The step-by-step deployment process we’ve covered gives you everything needed to get started, and the best practices shared will help you avoid common pitfalls. Your data science team will thank you for the improved collaboration, faster model iterations, and reduced operational overhead that this powerful combination delivers.


















