
Cloud-Native File Processing and Analytics with AWS Services
Modern businesses generate massive amounts of data daily, and traditional file processing methods can’t keep up. Cloud-native file processing with AWS services offers a scalable, cost-effective solution that transforms how organizations handle data workflows.
This guide is designed for developers, data engineers, and IT professionals who want to build robust automated file processing pipelines using AWS’s serverless architecture. You’ll learn practical approaches to handle everything from simple file transformations to complex analytics workloads.
We’ll start by exploring the core AWS file processing services like Lambda, S3, and Step Functions that form the backbone of serverless data processing. You’ll discover how these services work together to create efficient cloud data workflows that scale automatically with your needs.
Next, we’ll dive into building production-ready systems that combine AWS analytics services with automated processing pipelines. You’ll see how to set up real-time data processing, implement proper error handling, and optimize performance for different file types and volumes.
Finally, we’ll cover security best practices and walk through actual implementation examples that you can adapt for your own projects. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for implementing cloud-native architecture that handles your file processing and analytics requirements.
Understanding Cloud-Native Architecture for File Processing

Core Principles of Cloud-Native Design
Cloud-native architecture transforms how we approach file processing by embracing distributed, microservices-based systems that run entirely in cloud environments. Unlike traditional monolithic applications, cloud-native file processing systems decompose complex workflows into smaller, independent services that communicate through well-defined APIs. Each service handles specific tasks like file validation, format conversion, or data extraction, making the entire system more resilient and easier to maintain.
Event-driven architecture forms the backbone of cloud-native file processing. When files arrive in cloud storage, they trigger automated workflows without requiring persistent server instances. This reactive approach means your system only activates when needed, responding instantly to file uploads or processing requests. The decoupled nature ensures that if one component fails, others continue operating normally.
Container orchestration and immutable infrastructure principles ensure consistent deployment across environments. Your file processing logic remains identical whether running in development, staging, or production. This consistency eliminates the “it works on my machine” problem that plagues traditional file processing systems.
Benefits of Serverless File Processing Workflows
Serverless file processing workflows eliminate infrastructure management completely. AWS Lambda file processing functions execute your code in response to file events without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your processing logic, configure triggers, and the platform handles everything else—from scaling to security patches.
The automatic scaling capabilities prove particularly powerful for file processing workloads. When hundreds of files arrive simultaneously, serverless functions spin up instantly to handle the load. During quiet periods, costs drop to near zero since you’re not paying for idle servers. This elasticity matches perfectly with unpredictable file processing demands.
Development velocity accelerates dramatically with serverless approaches. Teams focus entirely on business logic rather than infrastructure concerns. Deploying new file processing features becomes as simple as updating function code, with no server configurations or capacity planning required. This rapid iteration cycle enables faster feature delivery and quicker responses to changing business requirements.
Scalability Advantages Over Traditional Systems
Traditional file processing systems struggle with variable workloads because they require fixed server capacity. During peak processing times, servers become bottlenecks, causing delays and potential failures. Cloud-native architecture eliminates these constraints through horizontal scaling that adapts automatically to demand.
AWS services like Lambda can process thousands of files concurrently, with each function instance handling individual files independently. This parallel processing approach dramatically reduces total processing time compared to sequential traditional systems. Large file batches that might take hours on traditional infrastructure complete in minutes through massively parallel cloud-native processing.
Storage scalability matches processing scalability seamlessly. AWS S3 provides virtually unlimited storage capacity that grows automatically as your file volumes increase. You never need to provision additional storage or worry about running out of space. The integration between storage and processing services creates smooth, uninterrupted workflows regardless of data volumes.
Cost Optimization Through Pay-Per-Use Models
Pay-per-use pricing models revolutionize file processing economics by aligning costs directly with actual usage. Traditional systems require ongoing payments for server capacity whether processing files or sitting idle. Cloud-native architecture charges only for active processing time and storage consumption.
AWS Lambda charges per request and execution duration, measured in milliseconds. A file processing function that runs for 100 milliseconds costs significantly less than maintaining a dedicated server for hours. This granular pricing model makes file processing economical even for sporadic or unpredictable workloads.
Storage costs scale proportionally with actual data volumes. AWS S3 pricing tiers reward larger volumes with lower per-gigabyte rates, while intelligent tiering automatically moves infrequently accessed files to cheaper storage classes. This dynamic optimization reduces storage costs without manual intervention or complex migration planning.
Resource optimization tools provide detailed cost breakdowns and usage patterns, enabling precise budget control. You can set spending limits, receive cost alerts, and analyze which file processing operations generate the highest expenses. This visibility enables continuous optimization that traditional systems rarely provide.
Essential AWS Services for File Processing Workflows
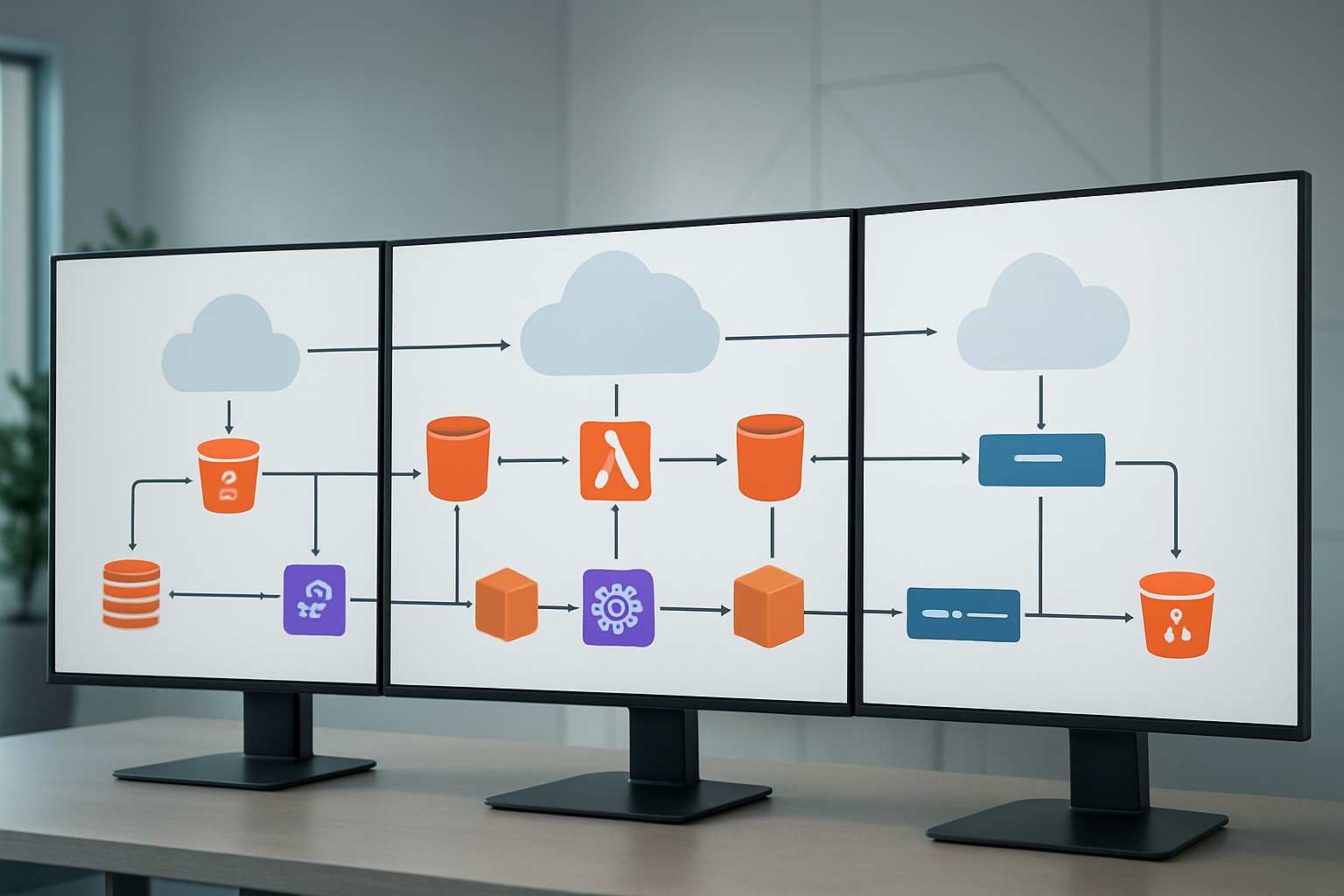
Amazon S3 for secure file storage and management
Amazon S3 serves as the foundational layer for cloud-native file processing workflows, offering virtually unlimited storage capacity with enterprise-grade security features. The service provides multiple storage classes that automatically optimize costs based on access patterns, making it perfect for processing files of varying sizes and frequencies.
S3’s event notification capabilities trigger downstream processing automatically when files arrive, enabling true serverless file processing automation. You can configure bucket policies and access controls with granular precision, ensuring sensitive data remains protected throughout the entire processing pipeline. The service integrates seamlessly with other AWS analytics services, creating a unified data ecosystem.
Cross-Region Replication and versioning features protect against data loss while maintaining compliance requirements. S3 Transfer Acceleration speeds up file uploads from global locations, reducing processing delays for time-sensitive workflows.
AWS Lambda for serverless processing functions
AWS Lambda transforms how we approach file processing by eliminating server management overhead entirely. These serverless functions scale automatically based on incoming file volumes, processing thousands of files simultaneously without capacity planning. Lambda supports multiple programming languages, allowing teams to leverage existing code libraries and expertise.
The pay-per-execution model makes Lambda incredibly cost-effective for variable workloads. Functions can process files directly from S3 triggers, transforming data formats, extracting metadata, or performing complex analytics operations. Memory and timeout configurations can be adjusted based on processing requirements, with functions scaling from 128MB to 10GB of memory.
Lambda’s integration with other AWS services creates powerful processing chains. You can easily connect functions to databases, message queues, and analytics platforms without managing infrastructure connections. Error handling and retry mechanisms ensure reliable processing even when dealing with corrupted or problematic files.
Amazon SQS and SNS for reliable message queuing
Amazon SQS provides the messaging backbone for robust file processing workflows, ensuring no files get lost during processing spikes. Standard queues handle high-throughput scenarios, while FIFO queues maintain strict ordering when sequence matters. Dead letter queues capture failed processing attempts, allowing for manual inspection and reprocessing.
Visibility timeouts prevent duplicate processing while allowing sufficient time for complex operations. Message attributes can carry metadata about files, routing them to appropriate processing functions based on file type, size, or priority level.
Amazon SNS complements SQS by enabling fan-out architectures where single file events trigger multiple processing paths. Email, SMS, and webhook notifications keep stakeholders informed about processing status. SNS topics can route messages to multiple SQS queues, Lambda functions, or external systems simultaneously.
Together, SQS and SNS create resilient messaging patterns that handle failures gracefully while maintaining high throughput. Batch processing capabilities reduce costs and improve efficiency for high-volume scenarios.
AWS Step Functions for orchestrating complex workflows
Step Functions provide visual workflow orchestration for multi-step file processing operations. The service coordinates Lambda functions, container tasks, and AWS service calls into reliable, auditable workflows. State machines handle complex branching logic, parallel processing, and error recovery automatically.
Express workflows optimize costs for high-volume, short-duration processing tasks, while standard workflows provide detailed execution history for compliance and debugging. Choice states route files through different processing paths based on content, size, or metadata. Parallel states enable concurrent processing of different aspects of the same file.
Built-in error handling includes retry mechanisms with exponential backoff and catch states that route failed executions to alternative processing paths. Wait states introduce delays for rate limiting or scheduled processing. The visual editor makes complex workflows understandable to both technical and business stakeholders.
Integration with CloudWatch provides detailed monitoring and alerting capabilities. Execution history maintains complete audit trails for regulatory compliance, showing exactly how each file was processed through the workflow.
Amazon EventBridge for event-driven architecture
EventBridge creates truly event-driven file processing architectures by connecting disparate systems through custom events. Rules filter and route events based on content patterns, enabling sophisticated processing logic without tight coupling between components. Schema registry ensures event consistency across different producers and consumers.
Custom event buses isolate different processing domains while maintaining central governance. Third-party SaaS integrations extend processing capabilities beyond AWS services, connecting to external analytics platforms, notification systems, or business applications.
Archive and replay capabilities support testing and disaster recovery scenarios. Event patterns can trigger multiple targets simultaneously, creating robust fan-out processing architectures. Cross-account event sharing enables enterprise-wide file processing coordination while maintaining security boundaries.
Scheduled rules enable time-based processing triggers, perfect for batch operations or cleanup tasks. Content-based filtering reduces noise by ensuring only relevant events reach specific processing functions, optimizing costs and reducing complexity.
Building Automated File Processing Pipelines

Setting up S3 event triggers for file uploads
AWS S3 event notifications form the backbone of automated file processing pipelines. When files land in your S3 buckets, these triggers instantly kick off your processing workflows without any manual intervention. You can configure event notifications for specific actions like object creation, deletion, or restoration, giving you precise control over when your pipeline activates.
Setting up these triggers involves configuring S3 bucket notifications through the AWS console, CLI, or Infrastructure as Code tools like CloudFormation. You can filter events by object name prefixes, suffixes, or even specific file extensions. For example, trigger processing only when CSV files are uploaded to the /incoming/ folder, or activate different workflows based on whether files land in /images/ versus /documents/ directories.
The most common event types for file processing include s3:ObjectCreated:* which covers all object creation events, or more specific ones like s3:ObjectCreated:Put for direct uploads. You can send these notifications to multiple destinations simultaneously – Lambda functions, SQS queues, or SNS topics – enabling parallel processing or routing to different systems based on your workflow requirements.
Consider implementing prefix and suffix filters strategically. This prevents unnecessary triggering and reduces costs while ensuring your automated file processing pipelines respond only to relevant files.
Implementing Lambda functions for data transformation
AWS Lambda functions serve as the processing engines in serverless file processing workflows. These functions automatically scale based on incoming file volumes and only charge for actual execution time, making them perfect for variable workloads. Your Lambda functions can handle everything from simple file format conversions to complex data transformations and enrichment tasks.
When building Lambda functions for file processing automation, consider the execution environment constraints. Standard Lambda functions have a 15-minute timeout limit and up to 10GB of temporary storage in /tmp. For larger files or longer processing tasks, you might need to break work into smaller chunks or use services like ECS Fargate for heavy lifting.
Memory allocation directly impacts performance and cost. Lambda allocates CPU proportionally to memory, so CPU-intensive transformations benefit from higher memory settings even if they don’t use all the RAM. Start with 1024MB and adjust based on CloudWatch metrics showing actual memory usage and execution duration.
Your transformation logic should handle common file processing scenarios:
- CSV to JSON conversion with schema validation
- Image resizing and format optimization
- PDF text extraction and indexing
- Log file parsing and structured data extraction
- Data cleansing and normalization
Environment variables help manage configuration without hardcoding values. Store database connection strings, API keys in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store or AWS Secrets Manager, and reference them in your Lambda functions for better security.
Creating error handling and retry mechanisms
Robust error handling separates production-ready cloud-native file processing systems from basic prototypes. Files can be corrupted, processing can fail due to temporary resource constraints, or downstream services might be temporarily unavailable. Your pipeline needs to gracefully handle these scenarios without losing data or requiring manual intervention.
Implement a multi-layered approach to error handling. Start with try-catch blocks in your Lambda functions to capture and log specific errors. Use structured logging with contextual information like file names, processing stages, and error details. This makes troubleshooting much easier when things go wrong.
Dead Letter Queues (DLQs) provide a safety net for failed processing attempts. When a Lambda function fails repeatedly, the triggering event gets routed to a DLQ instead of being lost. You can configure automatic retry attempts before sending events to the DLQ, giving transient errors a chance to resolve themselves.
Set up exponential backoff for retry mechanisms. Start with short delays and gradually increase them to avoid overwhelming struggling services. For example, retry after 2 seconds, then 4 seconds, then 8 seconds, up to a maximum delay. This pattern helps systems recover gracefully from temporary overload conditions.
Create different error handling paths for different failure types:
- Transient errors: Network timeouts, temporary service unavailability – retry with backoff
- Data quality issues: Malformed files, schema violations – route to manual review queue
- Configuration errors: Missing permissions, invalid parameters – alert administrators immediately
- Resource constraints: Memory limits, processing timeouts – consider alternative processing methods
Monitoring pipeline performance with CloudWatch
CloudWatch provides comprehensive monitoring for your automated file processing pipelines, giving you visibility into performance, errors, and resource utilization. Effective monitoring helps you identify bottlenecks, optimize costs, and maintain reliable service levels.
Start with built-in Lambda metrics like invocation count, duration, error rate, and throttles. These core metrics tell you how your functions perform under different loads. Set up CloudWatch alarms for error rates exceeding acceptable thresholds – typically 1-5% depending on your requirements.
Custom metrics provide deeper insights into your specific workflows. Track business-relevant metrics like files processed per hour, processing latency by file size, and data quality scores. Use CloudWatch’s PutMetric API or the AWS SDKs to emit these custom metrics from your Lambda functions.
CloudWatch Logs capture detailed execution information, but log volume can become expensive quickly. Implement log levels (ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG) and adjust based on your monitoring needs. Production systems typically log errors and warnings, while development environments might capture debug information.
Dashboard creation brings all metrics together in visual format. Build dashboards showing:
- Pipeline throughput over time
- Error rates by processing stage
- Resource utilization trends
- Cost metrics and projections
X-Ray distributed tracing helps you understand request flow through complex pipelines involving multiple AWS services. Enable X-Ray tracing to see exactly where time is spent and where errors occur in multi-service workflows.
Set up automated alerting for critical issues. CloudWatch alarms can trigger SNS notifications, automatically scale resources, or even initiate remediation workflows through Lambda functions. This proactive approach keeps your cloud data workflows running smoothly with minimal manual oversight.
Advanced Analytics Capabilities with AWS

Amazon Athena for SQL-based file analysis
Amazon Athena transforms serverless file processing by enabling direct SQL queries against data stored in Amazon S3 without requiring complex ETL processes or dedicated infrastructure. This powerful service works exceptionally well with various file formats including JSON, CSV, Parquet, and ORC, making it perfect for cloud-native file processing workflows.
You can analyze massive datasets stored in S3 using familiar SQL syntax, paying only for the data scanned during queries. Athena’s columnar storage optimization works particularly well with Parquet and ORC formats, dramatically reducing query costs and improving performance. The service automatically scales based on query complexity, handling everything from simple data exploration to complex analytical workloads.
Setting up Athena involves creating table schemas that map to your S3 data structure. Once configured, business analysts and data scientists can run sophisticated queries without needing specialized big data expertise. The integration with AWS Glue Data Catalog provides automatic schema discovery and metadata management, streamlining the entire analytics pipeline.
Performance optimization comes through partitioning strategies, compression techniques, and choosing appropriate file formats. Athena works seamlessly with other AWS analytics services, creating a comprehensive ecosystem for cloud storage analytics and automated file processing pipelines.
AWS Glue for ETL operations and data cataloging
AWS Glue serves as the backbone for ETL operations in cloud-native architectures, providing both serverless data processing capabilities and centralized metadata management through its Data Catalog. This fully managed service eliminates the complexity of provisioning and managing ETL infrastructure while offering powerful transformation capabilities for various data sources.
The Data Catalog acts as a central repository for metadata, automatically discovering schemas and data types across your file processing workflows. Glue crawlers scan data in S3, databases, and other sources, creating table definitions that other AWS analytics services can immediately use. This automated cataloging significantly reduces manual effort and maintains consistency across your data ecosystem.
Glue’s visual ETL editor allows teams to build complex data transformation jobs without extensive coding knowledge. The service supports both Python and Scala for custom transformations, offering flexibility for specialized processing requirements. Job scheduling and monitoring capabilities ensure reliable execution of data pipelines, with built-in error handling and retry mechanisms.
For organizations implementing serverless file processing, Glue provides dynamic scaling that adjusts compute resources based on workload demands. The service integrates seamlessly with AWS Lambda, enabling event-driven ETL processes that respond to new file arrivals in S3. This combination creates highly efficient, cost-effective data workflows that scale automatically with business needs.
Amazon QuickSight for interactive data visualization
Amazon QuickSight delivers business intelligence capabilities that complement file processing workflows by transforming processed data into actionable insights through interactive dashboards and visualizations. This cloud-native service connects directly to processed files in S3, Athena query results, and other AWS data sources without requiring data movement.
The service’s SPICE (Super-fast, Parallel, In-memory Calculation Engine) accelerates query performance for dashboard interactions, enabling real-time exploration of large datasets. QuickSight’s machine learning-powered insights automatically detect anomalies, forecasting trends, and highlight key findings within your processed data, making it valuable for organizations implementing AWS file processing services.
Dashboard creation involves intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces that business users can master quickly. The service supports various visualization types including heat maps, geographic displays, and custom calculations that adapt to different analytical needs. Embedded analytics capabilities allow organizations to integrate visualizations directly into applications, extending insights to end-users.
QuickSight’s scalability handles thousands of concurrent users while maintaining responsive performance. The pay-per-session pricing model makes it cost-effective for organizations with varying usage patterns. Integration with Active Directory and other authentication systems ensures secure access to sensitive analytical data within your cloud data workflows.
Integration with machine learning services
AWS machine learning services integrate seamlessly with file processing pipelines, enabling organizations to extract advanced insights and automate decision-making processes. Amazon SageMaker connects directly to processed data in S3, allowing data scientists to build, train, and deploy machine learning models without complex data movement operations.
The integration begins with automated data preparation through SageMaker Data Wrangler, which connects to your file processing outputs and provides visual data transformation tools. This eliminates the gap between data processing and model development, accelerating the machine learning lifecycle. SageMaker’s built-in algorithms work particularly well with structured data from ETL processes, supporting use cases like fraud detection, recommendation engines, and predictive maintenance.
Amazon Rekognition and Textract provide specialized AI capabilities for unstructured file processing, analyzing images, videos, and documents within your automated pipelines. These services extract text, detect objects, and identify patterns that traditional processing methods miss. The results integrate back into your analytics workflows, enriching datasets with AI-derived insights.
Amazon Comprehend adds natural language processing capabilities to text-heavy file processing scenarios. The service analyzes sentiment, extracts key phrases, and identifies entities within documents, creating structured data from unstructured sources. This integration particularly benefits organizations processing customer feedback, legal documents, or social media content through their cloud-native file processing infrastructure.
Security and Compliance Best Practices

Implementing IAM roles and policies for least privilege
Building secure cloud-native file processing systems starts with proper identity and access management. IAM roles and policies form the backbone of AWS security, controlling who can access what resources and when. The principle of least privilege means granting only the minimum permissions necessary for each component to function.
Create dedicated service roles for each AWS service in your file processing pipeline. Lambda functions should have their own execution roles with specific permissions to read from S3 buckets, write to CloudWatch logs, and invoke other services. Avoid using broad policies like AmazonS3FullAccess when your function only needs to read from specific buckets.
Use resource-based policies alongside identity-based policies for granular control. For example, restrict S3 bucket access to specific IP ranges or VPC endpoints. Cross-account access requires careful role assumption policies that specify trusted principals explicitly.
Policy conditions add another security layer. Time-based conditions can restrict access to business hours, while IP-based conditions limit access to corporate networks. MFA conditions ensure sensitive operations require additional authentication.
Regular policy audits using AWS Access Analyzer help identify unused permissions and overly broad access grants. The tool generates findings when policies grant access beyond your defined trust boundary, making it easier to maintain least privilege over time.
Encrypting data at rest and in transit
Data encryption protects sensitive information throughout your AWS file processing workflows. S3 bucket encryption should be enabled by default using server-side encryption with AWS KMS keys. This approach provides centralized key management and detailed audit trails for compliance requirements.
Choose between AWS-managed keys (SSE-S3), KMS customer-managed keys (SSE-KMS), or customer-provided keys (SSE-C) based on your security needs. KMS customer-managed keys offer the most control, allowing key rotation policies, cross-account access, and detailed CloudTrail logging of key usage.
Lambda functions can encrypt environment variables using KMS keys, protecting database connection strings and API credentials. When processing files, ensure temporary storage in /tmp directories uses encryption at rest through the underlying EBS volumes.
Transit encryption secures data movement between services. Enable HTTPS endpoints for all API Gateway configurations and ensure Lambda functions use TLS when calling external services. VPC endpoints for S3 and other AWS services automatically encrypt traffic within the AWS backbone.
CloudFront distributions should enforce HTTPS redirects and use modern TLS versions. Configure security headers like HSTS to prevent protocol downgrade attacks. For sensitive file uploads, implement presigned URLs with time-limited access and HTTPS-only policies.
Setting up VPC endpoints for private connectivity
VPC endpoints keep your serverless file processing traffic within the AWS network, reducing exposure to internet-based threats. Gateway endpoints for S3 and DynamoDB provide free, scalable connectivity without NAT gateway costs. These endpoints automatically route traffic through AWS’s private backbone.
Interface endpoints support additional services like Lambda, SQS, and SNS through private IP addresses within your VPC. Each endpoint creates elastic network interfaces in specified subnets, allowing fine-grained network access control through security groups and NACLs.
Configure endpoint policies to restrict access to specific resources. An S3 gateway endpoint policy might limit access to designated buckets used in your file processing pipeline, preventing data exfiltration to unauthorized locations. These policies work alongside IAM permissions for defense in depth.
DNS resolution requires attention when implementing VPC endpoints. Enable private DNS for interface endpoints to route service calls through private IPs automatically. Custom Route 53 hosted zones can provide additional DNS control for complex networking scenarios.
Monitor endpoint usage through VPC Flow Logs and CloudTrail. Flow logs reveal traffic patterns and potential security issues, while CloudTrail captures API calls made through endpoints. Set up CloudWatch alarms for unusual traffic volumes or unauthorized access attempts.
Security groups attached to interface endpoints should follow least privilege principles. Allow inbound traffic only from resources that legitimately need access, typically Lambda execution environments or EC2 instances running file processing applications.
Performance Optimization Strategies

Choosing Optimal File Formats for Processing Speed
The file format you choose can make or break your cloud-native file processing performance. When working with AWS analytics services, certain formats shine while others drag down your entire pipeline. JSON might be flexible, but it’s not your friend when processing millions of records. Parquet files typically deliver 3-5x faster query performance compared to JSON or CSV formats on services like Amazon Athena.
For analytics workloads, columnar formats like Parquet and ORC are game-changers. They compress better and allow AWS services to read only the columns you need, reducing I/O dramatically. If you’re dealing with time-series data, consider Delta Lake format for its optimization features and ACID properties.
Binary formats outperform text formats for large-scale processing. Avro works exceptionally well for schema evolution scenarios, while Protocol Buffers excel in high-throughput environments. For streaming data with AWS Lambda file processing, smaller file sizes with efficient compression can prevent timeout issues.
When serving data to end users, consider your access patterns. Frequently accessed data benefits from formats optimized for quick reads, while archival data should prioritize compression ratios.
Implementing Parallel Processing Techniques
AWS services are built for parallelization, but you need to architect your serverless file processing workflows to take advantage of this capability. Amazon S3’s multipart upload feature allows you to break large files into chunks that can be processed simultaneously by multiple Lambda functions.
Lambda’s concurrent execution model naturally supports parallel processing. Instead of processing a 1GB file sequentially, split it into 100MB chunks and trigger multiple Lambda instances. This approach reduces overall processing time from hours to minutes for large datasets.
AWS Step Functions orchestrates complex parallel workflows beautifully. You can fan-out processing tasks across multiple services – Lambda for transformation, Glue for ETL operations, and SageMaker for machine learning inference – all running simultaneously.
Kinesis Data Streams enables real-time parallel processing by automatically distributing incoming data across multiple shards. Each shard can be processed independently, scaling your throughput based on demand.
For batch processing, EMR clusters can distribute workloads across multiple nodes. Configure your cluster size based on data volume and processing complexity. Auto-scaling groups help manage costs while maintaining performance during peak loads.
Leveraging AWS Service Limits and Throttling
Understanding AWS service limits prevents bottlenecks in your cloud data workflows. Lambda has a default concurrent execution limit of 1,000 functions per region, but you can request increases based on your processing needs. Monitor your concurrent executions to avoid throttling during peak loads.
S3 request rates matter more than most developers realize. The service handles 3,500 PUT/COPY/POST/DELETE and 5,500 GET/HEAD requests per second per prefix. Design your object naming strategy to distribute requests across multiple prefixes, avoiding hotspots that trigger throttling.
API Gateway has rate limits that can impact file upload workflows. The default limit is 10,000 requests per second with burst capacity of 5,000 requests. Plan your file processing automation around these constraints or request limit increases.
DynamoDB’s read and write capacity units need careful planning. On-demand mode automatically scales but comes with higher costs. Provisioned capacity offers cost control but requires monitoring to prevent throttling during traffic spikes.
Kinesis has shard-level limits – each shard supports 1,000 records per second or 1MB per second for writes. Plan your stream partitioning strategy based on expected throughput to avoid producer-side throttling.
Memory and Timeout Configuration Best Practices
Lambda memory configuration directly impacts processing speed and cost. More memory means more CPU power – a 1,024MB function runs roughly twice as fast as a 512MB function for CPU-intensive tasks. Test different memory settings to find the sweet spot where performance gains justify the cost increase.
Timeout values should match your processing requirements. The maximum Lambda timeout is 15 minutes, perfect for most file processing tasks. Set timeouts based on file sizes and complexity – simple JSON parsing might need 30 seconds, while complex transformations could require several minutes.
Memory allocation affects more than just processing speed. Lambda functions with insufficient memory may fail unexpectedly or exhibit poor performance. Monitor memory usage in CloudWatch to identify optimization opportunities.
For AWS Glue jobs, memory configuration impacts the number of DPUs (Data Processing Units) allocated. Each DPU provides 4 vCPUs and 16GB of memory. Match your DPU allocation to data volume and transformation complexity.
Kinesis Analytics applications benefit from proper parallelism configuration. The service automatically scales based on input data rate, but you can optimize performance by adjusting the parallelism count for each operator in your application.
Consider memory-mapped files for large dataset processing in EC2-based solutions. This technique allows the operating system to handle memory management, reducing garbage collection overhead and improving performance for memory-intensive analytics operations.
Real-World Implementation Examples
Document Processing and OCR Workflows
Enterprise organizations handle thousands of documents daily, from invoices and contracts to medical records and legal papers. A major insurance company implemented a cloud-native file processing system using AWS Lambda file processing combined with Amazon Textract for OCR capabilities. Their workflow starts when documents arrive in Amazon S3, triggering Lambda functions that automatically classify document types and route them through appropriate processing pipelines.
The system uses Amazon Comprehend for entity extraction and sentiment analysis on textual content, while Amazon Rekognition handles image-based documents. For high-volume processing, they leverage AWS Batch to handle computationally intensive OCR tasks across multiple document formats. The entire automated file processing pipeline processes over 50,000 documents daily with 99.7% accuracy.
Key components include:
- S3 event notifications triggering serverless file processing workflows
- Step Functions orchestrating complex multi-stage document analysis
- DynamoDB storing metadata and processing status
- CloudWatch monitoring processing metrics and error rates
Media File Transcoding and Analysis Pipelines
Streaming platforms require robust cloud-native file processing solutions to handle video uploads, transcoding, and content analysis at scale. A popular video-sharing platform built their media pipeline using AWS Elemental MediaConvert for transcoding, combined with Lambda functions for preprocessing and quality validation.
Their cloud data workflows automatically detect uploaded video formats, extract thumbnails, generate multiple resolution outputs, and perform content moderation using Amazon Rekognition Video. The system processes petabytes of media monthly while maintaining cost efficiency through spot instances and intelligent scaling.
The architecture includes:
- S3 lifecycle policies managing storage costs across different access tiers
- AWS analytics services tracking viewer engagement and content performance
- Elastic Transcoder handling legacy format conversions
- CloudFront distributing processed content globally
Real-time analysis capabilities include face detection, celebrity recognition, and inappropriate content flagging, all integrated seamlessly into the transcoding workflow.
Log File Aggregation and Monitoring Systems
DevOps teams struggle with massive log volumes from distributed applications. A fintech startup created a comprehensive log processing system using Amazon Kinesis Data Streams to ingest logs from thousands of microservices. Their serverless data processing approach uses Kinesis Analytics for real-time pattern detection and anomaly identification.
The system automatically scales based on log volume, processing millions of events per minute during peak trading hours. Processed logs flow into Amazon OpenSearch for indexing and visualization, while critical alerts trigger immediate notifications through SNS.
Architecture highlights:
- Kinesis Firehose delivering logs to S3 for long-term storage
- AWS S3 data analytics enabling historical trend analysis
- Lambda functions parsing and enriching log data in real-time
- CloudWatch dashboards providing operational visibility
Machine learning models built with Amazon SageMaker analyze log patterns to predict system failures before they occur, reducing downtime by 85% compared to their previous reactive monitoring approach. The file processing automation extends beyond basic log collection to intelligent operational insights that drive proactive system maintenance.

Moving to cloud-native file processing with AWS opens up incredible possibilities for handling data at scale. You get access to powerful services like S3 for storage, Lambda for serverless processing, and advanced analytics tools that can transform raw files into valuable insights automatically. The combination of automated pipelines, built-in security features, and pay-as-you-go pricing makes it a smart choice for businesses dealing with growing amounts of file data.
Ready to get started? Begin small by setting up a basic S3 bucket and experimenting with Lambda functions to process your files. As you get comfortable with the basics, you can gradually add more sophisticated analytics and automation features. The beauty of AWS is that you can scale your solution as your needs grow, without having to rebuild everything from scratch. Your data processing workflows will become faster, more reliable, and surprisingly cost-effective once you make the switch.










