Overview
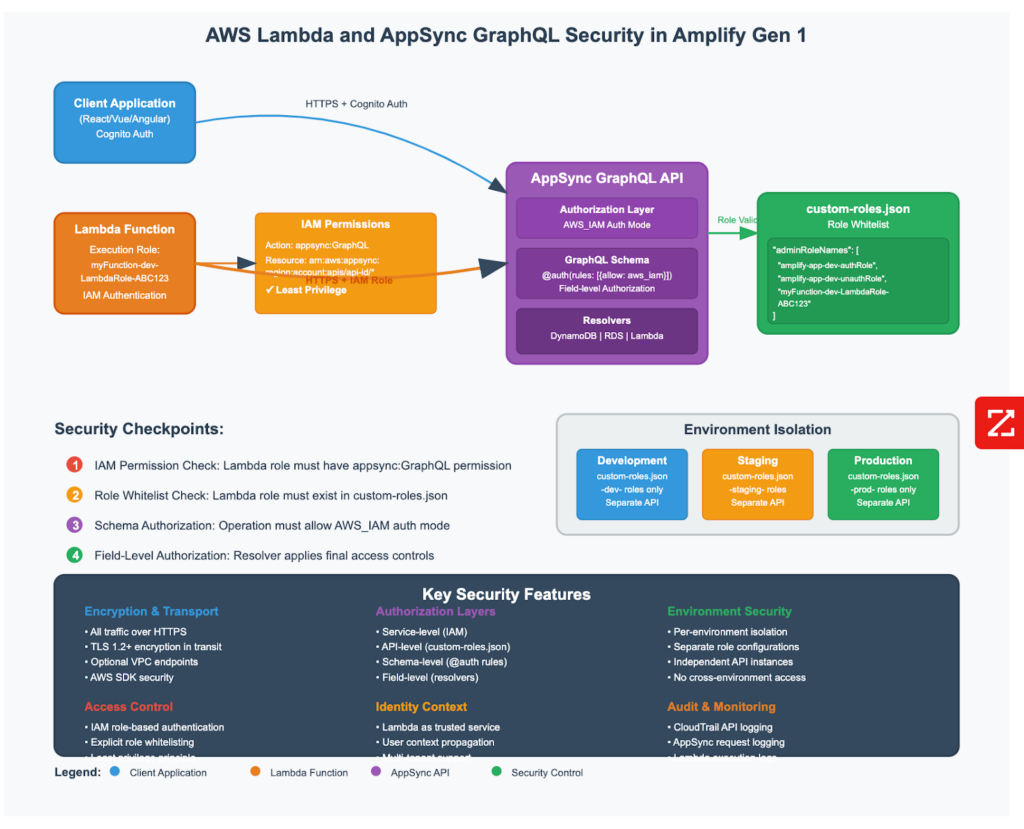
AWS Lambda functions in Amplify Gen 1 can securely interact with AppSync GraphQL APIs through a multi-layered security model that combines IAM authentication, explicit role whitelisting, and fine-grained authorization controls.
Core Security Architecture
1. IAM-Based Authentication
Lambda functions authenticate to AppSync using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) rather than client-side authentication methods. Each Lambda function receives an execution role that serves as its identity when making GraphQL requests.
Required IAM Permissions: The Lambda execution role must include specific permissions to access AppSync:
json
{
“Version”: “2012-10-17”,
“Statement”: [
{
“Effect”: “Allow”,
“Action”: [“appsync:GraphQL”],
“Resource”: “arn:aws:appsync:region:account:apis/api-id/*”
}
]
}
2. GraphQL Schema Authorization
The GraphQL schema must explicitly support AWS_IAM as an authorization provider. Operations that Lambda functions need to access must include IAM-based authorization rules such as @auth(rules: [{ allow: aws_iam }]).
3. Role Whitelisting via custom-roles.json
This is a critical security component unique to Amplify Gen 1. Lambda execution roles must be explicitly whitelisted in the API’s custom-roles.json file located at amplify/backend/api/[api-name]/custom-roles.json.
File Structure:
json
{
“adminRoleNames”: [
“amplify-myapp-dev-123456-authRole”,
“amplify-myapp-dev-123456-unauthRole”,
“myLambdaFunction-dev-LambdaRole-ABCDEF123456”
]
}
Role Management:
- Roles can be added automatically when using amplify add function
- Manual addition may be required for external Lambda functions
- Role names follow the pattern: [function-name]-[environment]-LambdaRole-[suffix]
Security Benefits and Controls
Secure Communication
- All Lambda-to-AppSync communication occurs over HTTPS
- Traffic is encrypted in transit automatically
- Optional VPC endpoints can keep traffic within AWS network boundaries
Least Privilege Access
- Lambda roles can be configured with minimal permissions
- Access can be restricted to specific GraphQL operations or data sources
- Fine-grained control over what each Lambda function can access
Environment Isolation
- Each environment (dev, staging, production) maintains separate custom-roles.json files
- Role configurations are environment-specific
- Prevents cross-environment access
Identity Context Propagation
Lambda functions can forward original user context from frontend applications, enabling AppSync resolvers to make authorization decisions based on both:
- Lambda’s IAM permissions (service-level authorization)
- End user’s identity and permissions (user-level authorization)
Security Workflow
- Lambda Creation: Function receives IAM execution role with AppSync permissions
- Role Whitelisting: Execution role added to custom-roles.json
- Schema Authorization: GraphQL operations configured with AWS_IAM auth rules
- Runtime Security: Lambda authenticates with IAM, AppSync validates against whitelist
- Operation Authorization: GraphQL resolvers apply field-level authorization
Critical Security Considerations
Whitelist Requirement: Without proper custom-roles.json configuration, Lambda requests will be rejected even with correct IAM permissions.
Admin-Level Access: Roles in adminRoleNames receive elevated privileges and can potentially bypass field-level authorization – use judiciously.
Trust Boundary: Lambda functions operate as trusted backend services with different security models than client applications.
This security model ensures that only authorized Lambda functions can access GraphQL operations while maintaining separation between service-level and user-level authorization, providing comprehensive protection for your AppSync API.
Security Architecture